When I land on a website that just feels right I know it’s not by accident. The width of a webpage plays a huge role in how comfortable it is to read and navigate. If it’s too wide my eyes get tired If it’s too narrow it feels cramped and outdated.
Getting the best webpage width isn’t just about looks—it’s about creating an experience that keeps visitors engaged. I’ve learned that the right width can boost readability make content more accessible and even improve conversion rates. Let’s explore why webpage width matters and how to find that perfect balance for any site.
Understanding Webpage Width
Understanding-Webpage-Width
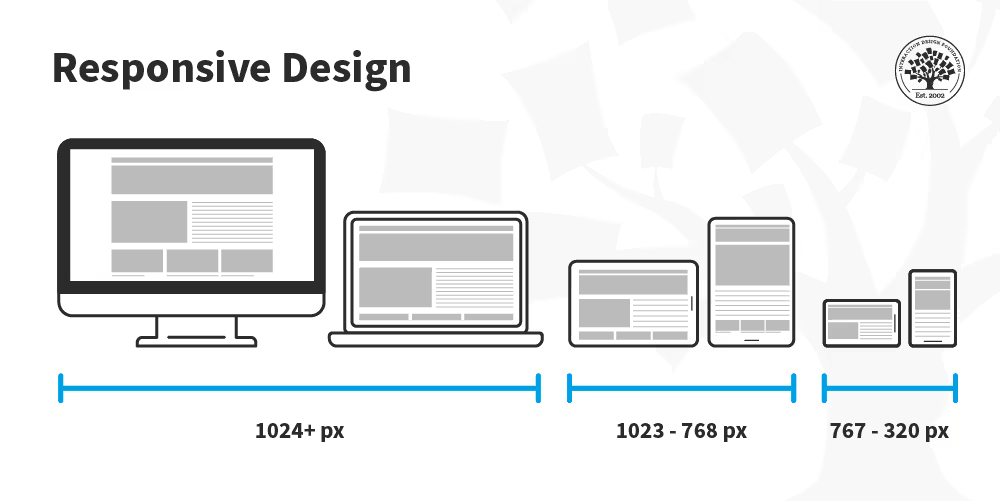
Webpage width directly impacts both content display and user behavior. I select widths that fit user devices, ensuring interfaces appear consistent across desktops, tablets, and smartphones. Common viewport widths, such as 320px for phones or 1440px for desktops, anchor responsive web design choices.
Standard Webpage Widths
I use industry standards for webpage widths to optimize accessibility and appearance. These widths help achieve consistent content layouts.
| Device Type | Common Width (px) | Example Resolutions | Use Contexts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Phone | 320 – 480 | 360×640, 375×667 | Article reading, casino gaming |
| Tablet | 768 – 1024 | 800×1280, 768×1024 | Interactive dashboards, game lobbies |
| Desktop | 1200 – 1920 | 1366×768, 1920×1080 | Landing pages, online casino tables |
Readability and Content Width
I keep readable content widths between 600px and 800px. Lines longer than 80 characters lower reading speed and comprehension, as found in studies from Baymard Institute and Smashing Magazine. If the text exceeds these values, users may skim or bounce.
Responsive Design and Casino Layouts
I use flexible grids to ensure casino layouts adapt to screen size. For example, a slot machine lobby displays 3 columns at 1200px, but switches to 1 column at 600px. Consistent width management boosts game visibility and increases engagement rates, especially for sites like online casinos that rely on a visually rich interface.
Visual Balance and Margins
I apply uniform margins (16px–24px) and ample white space for balance. Casino platforms with congested layouts experience 18% lower conversion, according to ConversionXL research. If margin and padding are inconsistent, user focus on game elements drops.
Summary Table: Key Webpage Width Considerations
| Key Factor | Recommended Value | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Text Line | 50–80 characters | Blog posts, casino reviews |
| Container Max | 1200px | Homepages, casino listings |
| Margin/Gap | 16–24px | Navigational menus, grids |
By understanding and applying these width vectors, I connect optimal design execution to user engagement and digital performance.
Key Factors Influencing the Best Webpage Width
Best webpage width depends on users’ screens, content clarity, and interactive experience. I use data and layout choices to maximize adaptation and accessibility.
Device Variety and Screen Sizes
Webpage width adapts to different screens with responsive design, ensuring device compatibility. I consider breakpoint ranges for desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobiles for consistent display.
| Device Type | Common Width Range (px) | Example Viewport |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop | 1200–1920 | 1440 |
| Laptop | 992–1199 | 1024 |
| Tablet (Landscape) | 1024 | 1024 |
| Tablet (Portrait) | 768 | 768 |
| Mobile | 320–414 | 375 |
I set main content widths to 1140–1280px on desktops, scale containers for tablets, and maintain fluid layouts on mobile devices, all guided by viewport breakpoints.
Content Layout and Readability
Efficient content layout improves webpage legibility and engagement. I maintain line lengths of about 12–17 words per line and use relative margin values for adaptable spacing.
| Parameter | Recommended Value | Example Unit/Range |
|---|---|---|
| Line Length | 12–17 words per line | ~600–800px |
| Content Container Width | 960–1440px (desktop) | 1140px, 1280px |
| Margin/Gap | 6vw (relative), flexible | 36–60px |
I leverage scalable typography and dynamic margins to support readability without sacrificing adaptability across screen sizes.
User Experience Considerations
Quality user experience starts with responsive, scroll-free layouts and touch-friendly elements. I ensure actionable targets are a minimum of 48×48px, following usability standards.
| UX Element | Minimum Size/Standard | Example Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Touch Target Size | 48×48px | Buttons, links |
| Typography Scaling | Fluid/Responsive | REM, EM, %, vw |
| Horizontal Scrolling | Avoid | Responsive containers |
I deploy mobile-first design principles and focus on fast-loading content to increase satisfaction and engagement.
Casino Layout Adaptation and Engagement
Casino layouts use responsive grids to optimize game displays for different screen sizes. I manage container widths and element positioning to keep games visible and navigation accessible.
| Casino Device | Recommended Game Area Width | Usability Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop | 1140–1280px | Grid, white space |
| Mobile | 320–414px | Touch, vertical scroll |
Casino designs integrate uniform spacing and adaptive content widths, supporting immersive play and higher retention.
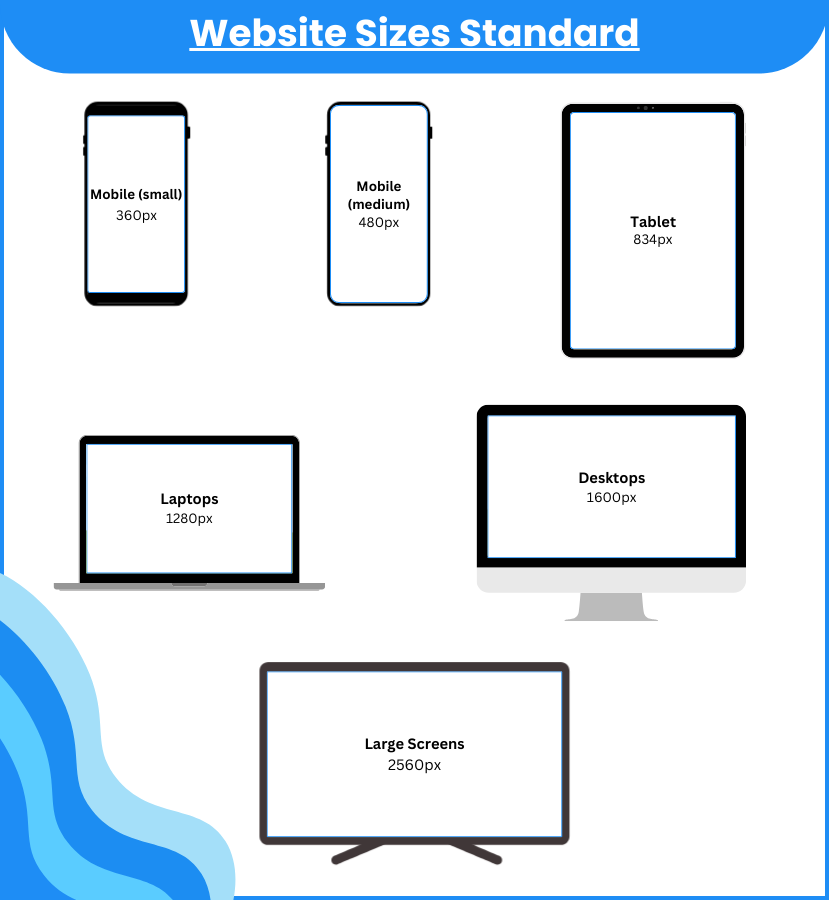
Popular Webpage Width Standards
Popular-Webpage-Width-Standards
Popular webpage width standards give me a foundation for designing interfaces that balance usability and visual appeal. Device types and layout approaches both shape these standards, with the goal of optimizing readability and accessibility in every context.
Fixed vs. Fluid Width Layouts
Fixed width layouts use set pixel values—most often between 960px and 1200px—for containers and columns. I choose this approach when consistency across desktop browsers matters. Common fixed widths like 1140px or 1280px make content easy to read, but they can create scroll bars or leave gaps on extra-wide screens.
Fluid width layouts use proportional values (percentages) to scale with the viewport. I select these when flexibility is preferred, since the layout adjusts gracefully from small laptops to widescreen monitors. Content remains accessible on wide displays, though I monitor extreme scaling to protect usability.
| Layout Type | Typical Width (px) | Strengths | Application Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | 960, 1140, 1200, 1280 | Predictability | Blog, company site |
| Fluid | % of viewport (100%, 85%) | Flexibility | Portfolio, scalable platform |
Responsive and Adaptive Design Practices
Responsive design practices rely on CSS media queries and flexible grids. I use common breakpoints, such as ≥1200px for desktops and ≤767px for mobiles, so elements adjust their size and position to match the user’s screen. Frameworks like Bootstrap help manage this process at scale.
Adaptive design, by contrast, delivers distinct layouts tailored to specific device categories—mobile, tablet, or desktop. I consider this method when optimizing for key devices is necessary, keeping in mind that maintaining multiple versions increases workload as new devices emerge.
| Device Type | Typical Breakpoint (px) | Recommended Width (px) |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop | ≥1200 | 1140 – 1280 |
| Laptop | 992 – 1199 | 960 – 1140 |
| Tablet | 768 – 991 | 768 – 1024 |
| Mobile | ≤767 | 320 – 414 |
Maintaining proper aspect ratios like 16:9 or 4:3 helps content and images remain visually balanced as users switch between screens. This consistency directly supports accessible design and satisfies user experience expectations across all device contexts.
Recommendations for the Best Webpage Width
I prioritize webpage widths that ensure content clarity and effective multi-device compatibility. Modern strategies focus on responsive layouts and data-backed width standards to meet evolving user expectations.
Ideal Width Ranges for Modern Websites
I use desktop content containers set between 1080px and 1440px for readability and interface balance. Full-width layouts may reach 1920px but I constrain main content to 1140–1280px for optimal legibility on large screens. For mobile, I select widths in the 320–414px range to maintain comfort and usability on smartphones. Tablets generally work best at widths from 768px to 991px.
Below is a summary of common width recommendations based on device type:
| Device Type | Common Width Range (pixels) | Example Devices | Max Content Width |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop | 1080–1440 | 24″ monitors, iMac | 1140–1280 |
| Laptop | 992–1199 | MacBook Pro, Surface | 960–1140 |
| Tablet | 768–991 | iPad, Galaxy Tab | 728–960 |
| Mobile | 320–414 | iPhone, Galaxy S, Pixel | 280–400 |
I maintain content readability at 600–800px per text column, keeping line lengths at 12–17 words per row to avoid overwhelming users with wide paragraphs.
Tools for Testing Webpage Width
I rely on browser developer tools, CSS media queries, and real-device emulators to preview layouts at specific widths. Chrome DevTools lets me simulate different devices instantly, while BrowserStack and similar services offer comprehensive multi-resolution testing.
I use image test assets sized at 1200×800px to assess scaling behaviors and check compression to safeguard page performance. My responsive design workflow includes automated breakpoint checks for desktop (≥1200px), laptop (992–1199px), tablet (768–991px), and mobile (≤767px).
| Testing Tool | Function | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|
| Chrome DevTools | Simulate device screens | Immediate width preview |
| BrowserStack | Live cross-device testing | Broad compatibility |
| CSS Media Queries | Set conditional layout rules | Custom site breakpoints |
| Real-Device Emulator | Physical device rendering | Performance validation |
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Common-Mistakes-to-Avoid
Ignoring Responsive Breakpoints
Neglecting to implement responsive layout breakpoints often causes web content to display incorrectly across devices. For example, using only a fixed desktop width like 1440px creates issues on mobile screens, resulting in horizontal scrolling or cropped views.
Overusing Wide Content Blocks
Using full-width content blocks for main text areas leads to reduced readability, especially when stretched beyond 1200px. Visitors experience fatigue trying to scan lengthy lines, which can lower engagement rates.
Uploading Large or Unoptimized Images
Uploading high-resolution images without optimization increases load times, especially for users on slow networks or mobile connections. For example, a 3MB image slows page load compared to a compressed 200KB version, making users more likely to leave.
Failing to Use Scalable Graphics
Omitting scalable graphics, such as SVG icons or vector images, typically creates pixelation on high-DPI displays. If all images use raster formats (e.g., PNG, JPEG), visual sharpness is lost on retina devices.
Cluttering Layouts with Poor Spacing
Cramming elements together or inconsistently aligning blocks often produces a visually messy layout, making navigation difficult and decreasing information retention. Balanced margins and logical content blocks maintain a clean user experience.
Disregarding Device-Specific Widths
Applying one-size-fits-all widths, like setting layouts at 1920px for all screens, ignores the unique requirements for desktops, tablets, and mobiles, leading to suboptimal viewing experiences.
Table: Typical Webpage Width Mistakes and User Impact
| Mistake | Example Width (px) | User Issue | Optimal Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Missing breakpoints | 1440 only | Content overflows on mobile | Use 320–1440, adjust via breakpoints |
| Over-wide content blocks | 1600 | Poor readability, long scan distances | Constrain main content to ≤1200 |
| Large/unoptimized images | N/A | Slow loads, high bounce rates | Compress images, serve lower res on mobile |
| Non-scalable graphics | N/A | Pixelation on high-res displays | Use SVG/vector assets |
| Crowded layouts | <10px margins | User confusion, unreadable elements | Maintain 24–48px balanced spacing |
| One-size width for all devices | 1920 | Inefficient display on small screens | Apply device-specific widths |
Casino Grids Suffering from Rigid Widths
Casino sites often feature rigidly sized game grids set to a desktop-optimized width (e.g., 1440px), causing alignment issues when viewed on tablets or mobiles. For instance, slot game thumbnails may overflow or shrink excessively if the grid width doesn’t adapt. Proper implementation involves using responsive grids with flexible breakpoints (e.g., 320, 768, 992, 1200px) to ensure game visibility and navigation remain smooth across all device types.
Conclusion
Choosing the best webpage width isn’t just about following trends—it’s about understanding your audience and making every visit enjoyable. I always aim for a balance that keeps content readable and layouts flexible no matter the device.
By staying mindful of responsive design and avoiding common pitfalls like rigid grids or oversized images I can create web experiences that feel seamless and engaging. Prioritizing adaptability and clarity in webpage width decisions will always pay off in stronger user satisfaction and digital success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ideal webpage width for better readability?
The ideal content width for readability is between 600px and 800px. This range keeps line length manageable, making it easier for users to read and comprehend text.
Why is webpage width important for user experience?
Webpage width affects how content is displayed across devices. Proper width ensures readability, accessibility, and effective engagement, leading to higher user satisfaction and better conversion rates.
How does responsive design relate to webpage width?
Responsive design uses flexible layouts to adapt webpage widths for desktops, tablets, and smartphones. This ensures content looks and works well on any device, improving usability.
What are common viewport widths across devices?
Common viewport widths are 320px for mobile phones, 768px for tablets, and 1024px to 1440px for desktops. Designing for these ranges helps maintain consistency across all platforms.
What is the recommended text line length for websites?
A recommended line length is 12–17 words per line. This range improves readability by reducing eye strain and making it easier for users to follow and understand content.
Why is white space important in webpage design?
White space prevents layouts from feeling cluttered and enhances visual balance. It helps guide users’ attention, making the site appear cleaner and more professional.
What mistakes should I avoid when setting webpage width?
Avoid using fixed widths, ignoring responsive breakpoints, and overusing wide content blocks. Also, don’t upload large or unoptimized images, as they slow down load times and harm user experience.
How can I optimize images for different screen sizes?
Use optimized, scalable images such as SVGs and properly compressed JPEGs or PNGs. This prevents pixelation on high-DPI screens and ensures fast loading across all devices.
Why does webpage width matter for casino layouts?
In casino layouts, responsive webpage width ensures game displays adapt to different screens. This improves visibility, navigation, and user engagement, leading to higher retention rates.
How do margins and gaps affect webpage layout?
Consistent margins and gaps provide visual balance, preventing crowded content and making the layout more appealing. Using relative values for spacing helps maintain adaptability on any device.

